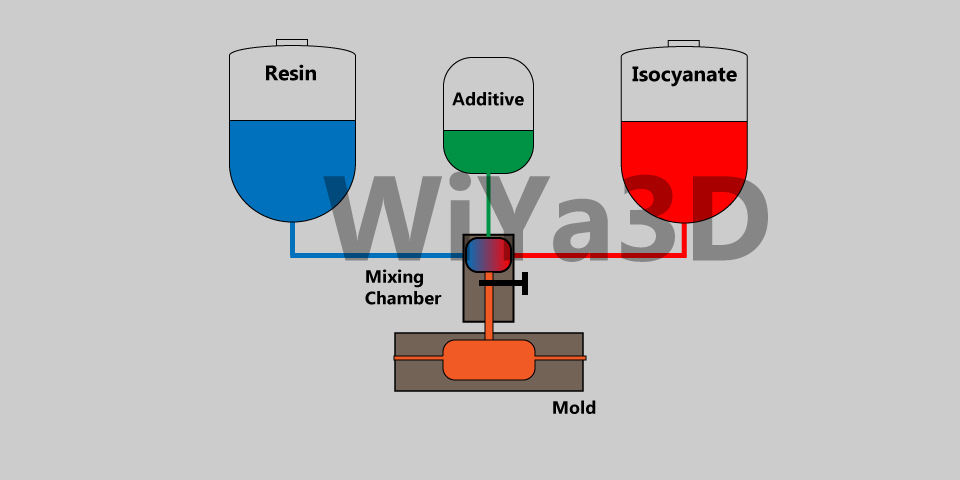
Reaction injection molding (RIM) is a manufacturing process used to produce plastic parts and components. It is similar to traditional injection molding, but instead of injecting a single polymer material into the mold cavity, RIM uses two or more liquid polymer materials that are mixed and reacted inside the mold to form the final product.
Reaction injection molding (RIM) is a relatively new production technique invented by Bayer in 1969.It is a method of generating structural plastic foams. This approach has developed into a leading plastic molding technique enabling a wide range of manufacturing and chemical processes. In the modern era, RIM is used to produce high-quality, relatively low volume plastic, foam & for rubber items. RIM chemically bonds two or more materials to form a polymer prior to inserting it into the mold.
During RIM process, firstly molten two polymers injected to mixing chamber with high pressure. And added some additives to react efficiently. Then the mixture of polymer is forcing into a designed mold to create thermoplastic resin components, under low pressure. The relatively high pressures are used to align the die plates of the mold or fixed separately in order to avoid asperities, flashing in the end product. RIM manufactures tougher, thicker, lighter, complex, flexible and more versatile parts at a lower cost that requirement of the low volume production. Although reaction injection molding is low pressure molding technique compare with high pressure injection molding.
How RIM Works
Reaction injection molding is a multi-stage technique with many stages as compared to traditional injection molding. The mixture of two liquid polymer materials (Resin & Isocyanate) inserted into a formulated mold is usually involved with the high-pressure impingement process. At the start, two or three forms of molten polymer, such as poly – isocyanate and resin compounds, are dumped into separate containers fitted with temperature and monitoring systems. The fluids are then discharged and pass through a measuring channel that regulates pressure, flow, air bubble and transfers to the molten polymer to a blending head/mold.
The mixer is usually pressurized to impact the rubber between 1500 and 3000 psi. After the reactants are combined, they are injected to molds with relative low pressure. The blender prevents emitting reactants until the process is done. The mold has an exothermic chemical reaction (heat-generating), which helps in the polymerization of plastics. The part of the polymer is cast out of the mold as it solidifies or ‘cures’.
Curing is done at low temperatures. Besides the necessary heat to produce the molten plastic, the reaction molding process is relatively cool. RIM contains chemical energy generated by polymerization rather than thermal energy. Typically, titanium, aluminum, or nickel molds are used, that are tightened with a lightweight press. Since the polymer cures in less than a minute, it enables rapid manufacturing and quick mid-volume production cycles.
RIM Process can Produce Three Types of Parts
- Rigid, structural, or decorative polyurethane foam sections, generally having a thick integral skin around a lower density core
- Pieces made of solid polyurethane elastomer with fragile wall portions
- Microcellular elastomer sections, which are thin-walled cellular products with a thick integral skin covering a lower density nucleus
Types of RIM Processes
- Reinforced Reaction Injection Molding (RRIM)
The technique is known as the strengthened reaction injection molding as it applies strengthening agents to the mixture. Glass fibers and mica are two common reinforcing agents. This method is most commonly used to make durable foam vehicle frames.
- Structural Reaction Injection Molding (SRIM)
It involves two highly reactive plastics having a low viscosity. These materials are mixed at high velocities in a mixer prior to the mixture being poured into a closed mold cavity.
Difference between Traditional and Modern Injection Molding
The method of injected molten plastic into a mold is known as injection molding. In Reaction injection molding, thermoset polymers are used as injected material. The injected material is cured in RIM, while in traditional Injection molding, plastic material is rapidly cooled and harden without using a curing agent.
RIM is similar to injection molding, except thermosetting polymers are used instead of thermoplastics. Reaction Injection molding will create components that typically cannot be generated using traditional IM processes: thick and thin-walled components, rolled cores, and much more. Lightweight parts are made using RIM. The choice of materials is the basis for the selection of process. Polyurethane, for example, is one of the most common RIM products.
Applications
- RIM can be used to produce PU, urea-formaldehyde, styrene class resin, nylon, and epoxy resin for car components, office materials, computer cases, furniture, and audio devices.
- It is perfect for manufacturing plans requiring large components.
- Manufacturing cycle speeds, cost-efficiency, and machine design will decide the process selection
- RIM is appropriate for the molding of large pieces with flat walls with thickness, and minimal injection strain
- RIM-manufactured steering wheels, armrests, body frameworks, dashboards, bumpers, gauges, and side panels are used by many automobile manufacturers
- All RIM materials exhibit elastomeric properties, making them ideal for use in household items, cooling and heating devices, and recreational equipment like water skis
- Reaction molding allows part reduction, enhances the manufacturing techniques, and reduces the need for secondary devices. This has been used by several industries to produce in-metal parts, such as hinges and frames
Advantages of RIM Process
- Lightweight Material
Polymer products made with reaction injection molding are generally considered to be lightweight and durable. In comparison, conventional injection molding materials are stainless steel, aluminum, or sheets (SMC). The weight reduction has several advantages in various industries.
- Large Parts
A car that contains dashboards, wiper cowl, bumpers or polyurethane rear bumper would save the driver and business thousands of dollars more efficiently than a vehicle with heavy materials. Lifting, operation, and handling of machinery consisting of such lighter materials are more efficient.
- Durable Product
The materials are stable, resilient, strong, durable, and long-lasting, capable of deforming and resisting impact and wear. Despite years of exposure to elements, it maintains its original form.
- Good Surface Finish
RIM enables the production of high or low gloss eye-catching finish. The products manufactured by RIM also include excellent thermal and acoustic insulators, thereby increasing their utility in a broad range of industrial sectors. It gives class ‘A’ surface finish.
- Rapid Prototyping
With lead times of 3-15 days, excellent prototypes can be produced at a much lower cost than conventional molding. RIM has a fast-processing time (0.5–0.6 min).
Disadvantages of RIM Process
- High Tool Costs / Initial Setup Cost
The costs for tools and raw materials are high due to the necessary design, tooling, and testing.
- Long set up lead times
An extensive testing is required in injection molding. It requires extra processing time
- Requires careful consideration
The injection molded plastic components must be carefully manufactured and handled. For example, avoid undercutting and rough edges, use uniform wall thicknesses to avoid cooling differences leading to deficiencies such as sink labels.
Concluding Remarks
The RIM process is suitable for manufacturing large products with low volume required, that are relatively complex forms, smooth finishes, and low-weight high-strength characteristics of the components. For easier recycling and re-use, injection-molded plastic is easily available and distributed across the geographic range. For the manufacturing of molded bulk parts, there is no commercially competitive alternative available. Injection molding is especially useful for a high-volume assembly projects, that containing large number of small parts.
One of the key advantages of RIM is its ability to produce parts with a wide range of physical properties. By carefully selecting the polymer materials and the proportions in which they are mixed, it is possible to create parts with different strength, stiffness, flexibility, and other properties. This allows RIM to be used for a wide range of applications.
Another advantage of RIM is its ability to produce parts with a high level of dimensional accuracy and surface finish. Because the polymer materials are mixed and reacted inside the mold, the final product is formed in a single step, with no need for additional post-processing or finishing. This allows for the production of parts with a smooth and consistent surface quality.
Overall, RIM is a valuable manufacturing process that offers many advantages over traditional injection molding. Its versatility, efficiency, and precision make it a popular choice for the production of a wide range of plastic parts and components.