What is Ergonomics?
Ergonomics is the scientific study of people’s efficiency in their working environment. It aims to design products, systems, and environments to fit the needs and abilities of the people who use them. In the field of product design, ergonomics plays a crucial role in creating products that are both functional and comfortable to use.
The ultimate target of almost every company/manufacturer is the end-user. Meanwhile, ergonomics is all about what the end-user thinks and feels in terms of usability, safety, productivity, and attractiveness of the product. It is a user-centered design, and it has human beings as its principal focus.
Ergonomics for Product Design
Inclusion of ergonomics consideration in the product design is of paramount concern for companies around the world. Today the companies are taking into consideration the importance of workers’ health.
In product design ergonomics, the subject is the end-user, and the object is the product used by the end-user. In this interconnection between the product and user, the psychological, physical, and anthropometric factors must be investigated.

There are several key principles of ergonomics that product designers should consider when designing a product. such as,
- Human Factors: This refers to the physical, cognitive, and social characteristics of the users of the product. Product designers should consider the size, strength, and abilities of the users, as well as their level of training and experience.
- Anthropometry: This refers to the measurement of the human body and its parts. Product designers should consider the dimensions of the human body, such as arm length and hand size, when designing products that will be held or operated by hand.
- Biomechanics: This refers to the study of the movement and function of the human body. Product designers should consider the natural movements and postures of the body when designing products that will be used for prolonged periods of time.
- User-Centered Design: This refers to the practice of designing products with the user in mind. Product designers should consider the needs and preferences of the users, as well as any potential barriers to use, when designing a product.
There are several tools and techniques that product designers can use to ensure that a product is ergonomically designed. These includes,
- Human Factors Analysis and Evaluation (HFE): This is a systematic process for evaluating the human factors of a product. It involves collecting data on the users of the product, analyzing the data, and making recommendations for design changes based on the analysis.
- Prototyping: This involves creating a physical model of the product to test and evaluate its ergonomics. Prototyping allows designers to get feedback from users and make any necessary changes before the final product is produced.
- User Testing: This involves having users test and evaluate the product to identify any issues with its ergonomics. User testing can be conducted in a variety of ways, including usability testing, user interviews, and focus groups.
Measurements To Consider on Ergonomically Improve Design
Following describe some of measurements & size that need to consider. When design for product for end user. Those human factors will defend on region to region and person to person. Although it’s need to get more accumulated or average value for target product design.
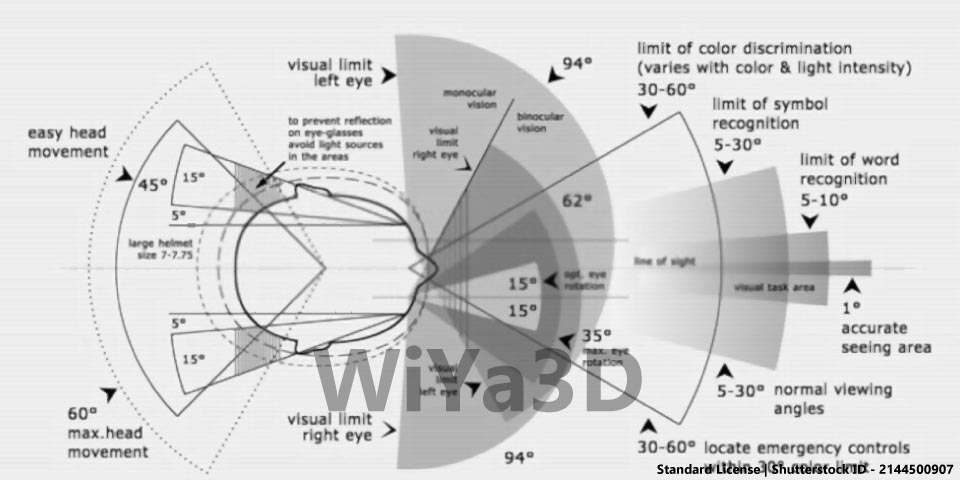
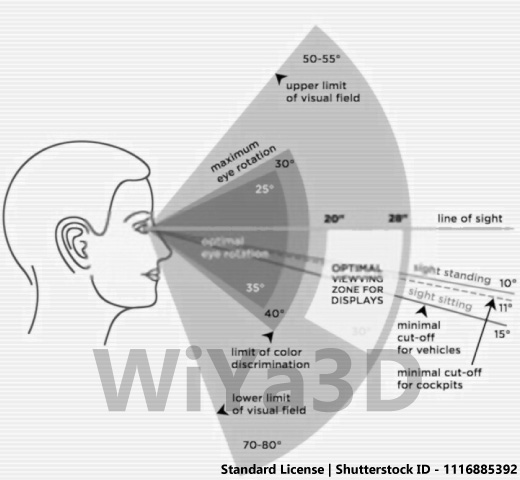
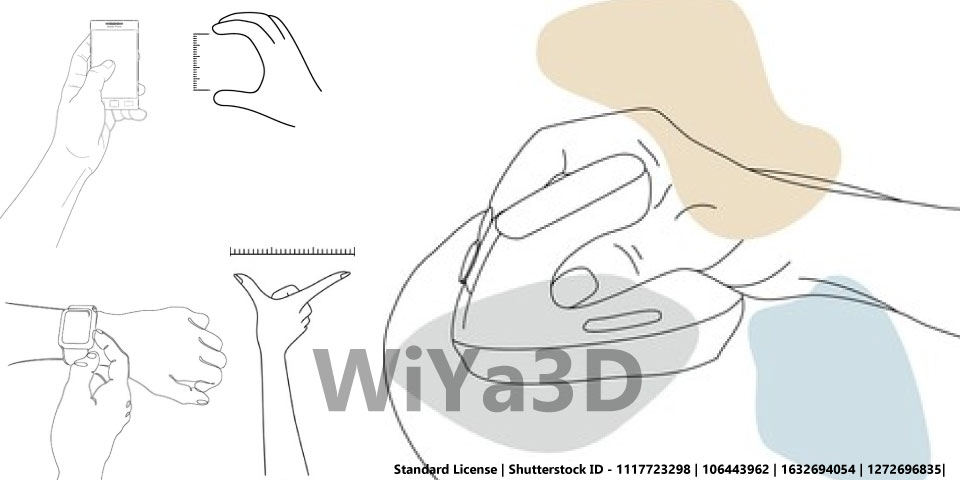
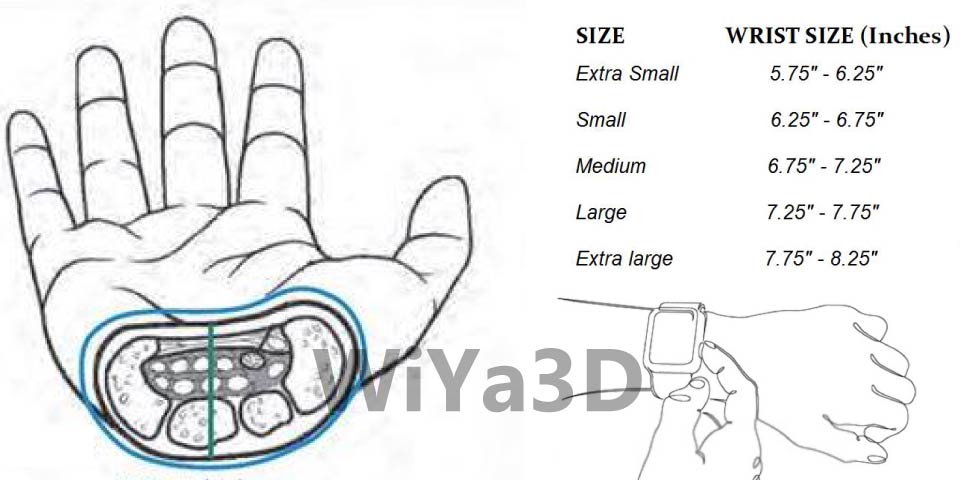
Importance of Ergonomic in Product Design
Ergonomic consideration in the design of products is advantageous, by the security, usability, health, efficiency, and emotional factors of the end-users are enhanced. Which directly connected to the functionalities and productivity.
The accidents and mishaps, potential malfunctions, and high costs are significantly reduced by considering ergonomic factors. Suppose the users are comfortable with the product or equipment both physically and mentally, no doubt. In that case, it leads to optimum functional effectiveness and performance.
Bio-Mechanical Simulations in Ergonomics Design
The biomechanical and physical perspective of humans is always associated with psychological behavior. Physical exercise and workload cause tiredness, discomfort, and unease in the body. These unwanted situations are avoided when the body relaxes.
An enormous number of biomechanical problems such as Cumulative Trauma Disorder (CTDS) caused due to muscle fatigue are associated with the product’s inefficiencies, lack of capabilities, and poor design.
Similarly, musculoskeletal disorders (MSD) are caused when a user is doing a continuous and repetitive job. When there is no ergonomically correct evaluation involved in the equipment design, the users are subjected to unwanted and unusual postures, contact stress for a prolonged period, and forced vibrations.
The initial mild effects later convert to severe chronic problems. To reduce workers’ occupational health concerns, we must quantify the allowable stress and fatigue level leading to ergonomically correct postures and hence increased comfort.
Outstanding Instances
- Many researchers have tried to change the ergonomic set up for a chair or a car seat to make it more comfortable and user-friendly. Some have proposed a seat-buttock model where the contact pressure and stress distribution at the buttock-seat interface were investigated using the Finite Element Analysis (FEA) technique.
- Using the ergonomic assessment techniques, there are many investigations possible. For example, ergonomists have developed a relation between the pressure distribution in the human body and the user’s relaxation and comfort level.
- Similarly, an example of hand ergonomics can be taken where an FEA Model of the hand is developed in close approximation with a real one. This model can represent the soft tissues of the hand, as well.
Do these features improve its usability and the end user’s comfort?
The answer is NO because more and more functions make it complicated, leading to poor usability. So there must be a compromise between usability and functionality, and that’s where ergonomics should come in the early stages of the product design process.
On the other hand, ergonomists continuously assess the impact of applied ergonomic design on the end-users. This continuous ergonomic assessment makes the products safe and usable. Remember, when the design is finalized, it is difficult to introduce changes into the design due to high costs and design complications.
Ergonomists, when continuously assessing the effects on product ergonomics, either use experimental prototypes or numerical models. Experimental testing is the expensive one and is being replaced with numerical and digital testing faster because of small-time delays and fewer costs.
Design Guide for Ergonomically Improve Product
The ergonomic product design process generally consists of the following steps, which applicable for any product design (Office Chair in the present but is applicable for any Product Design):
1. Approaching the users for data Collection
Surveys and questionnaires are prepared to approach associated users to collect office chair complaints, requirements, and other anthropometric factors and dimensions. The detailed lists for each of these attributes are prepared to consider quantitatively and qualitatively the required factors.
2. Investigate the Problem
After the data collection, we try to recognize, delimit, and formulate the problem to have a valid and reliable customer identification of the actual requirement.
3. Product Planning
The customer needs are further refined in this step. The method of Quality Function Deployment (QFD) is applied. QFD is the transformation and matching of customer requirements to the product design variables, which may involve mathematical interpretations.
4. ANFIS and Concept Design
After the QFD, it is time to inter-relate the design attributes to customer comfort and satisfaction. For this purpose, a technique called ANFIS, which stands for Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System, is used. ANFIS is a fuzzy inference based on neural networks.
The coordination between the neural networks and fuzzy systems can help us in approximating non-linear functions. After the analysis, the concepts are evaluated and refined, followed by a detailed design.
5. Prototyping, testing, and Verification
This stage can be either numerical or experimental. In experimental testing, a prototype of the office chair is prepared, evaluated with a user manual that later undergoes conditional modification and retesting. In cases of numerical testing, the same steps are repeated but numerically.
6. Product Production
After executing step-5 successfully, we manufacture the product on a large scale, keeping in mind all the manufacturing parameters. i.e., selecting the materials and suppliers, technical design trials, and documentation, etc.
7. Customer Support
Now that we have the finished product. It is dispatched to the end-user with customer support to train the end-users, maintain the product, monitor product performance, and receive product reviews.
Overall, ergonomics is a crucial aspect of product design that helps to ensure that products are functional, comfortable, and easy to use. By considering the human factors, anthropometry, biomechanics, and user-centered design, product designers can create products that are well-suited to the needs and abilities of their users.







