What is Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics is a subfield of fluid mechanics concerned with the study of moving liquids and gases around the objects and how interacts with it. Which affects everything, including aircraft, ships, rockets, missile fired, cars, kite flying in the sky and birds, that moves through the air & water.
Role of Aerodynamics
The industrial sector is currently the primary consumer of fossil fuels in the form of petrol and diesel. Automotive industries are trying to maximize fuel efficiency using various methods, and one of them is Aerodynamics. It has become necessary in the coming years. Therefore, one of the most significant factors of moveable body design is the drag coefficient (Cd).
Aerodynamic Consideration in Design
When designing a vehicle or other object that will move through the air or fluid medium, aerodynamic considerations are critical. The shape of the object can have a major impact on its performance and efficiency. For example, a vehicle with a streamlined shape will be able to move through the fluid more easily and with less resistance than a boxy vehicle with sharp corners.
In order to design an object with good aerodynamics, engineers must carefully consider the shape and surface texture of the object. Smooth, curved surfaces are typically more aerodynamic than rough or sharp surfaces. Additionally, the position of the object’s center of gravity can also have an impact on its aerodynamics.
The main aim is to reduce wind and wind resistance, limit noise emissions, avoid unnecessary lifting force and simplify the various causes of high risk. In this case, air is also considered to be liquid. For certain classes of hustling vehicles, it might likewise be imperative to create downforce to improve foothold and hence cornering capacities. There are different contrasts between auto aerodynamics and aircraft.
Regardless of the speed of movement of the moving object, it takes a certain amount of energy for the moving object to move in the air. This energy is used to defeat a force known as drag. The resistance in vehicle aerodynamics basically contains three forces Drag, Lift & Thrust.
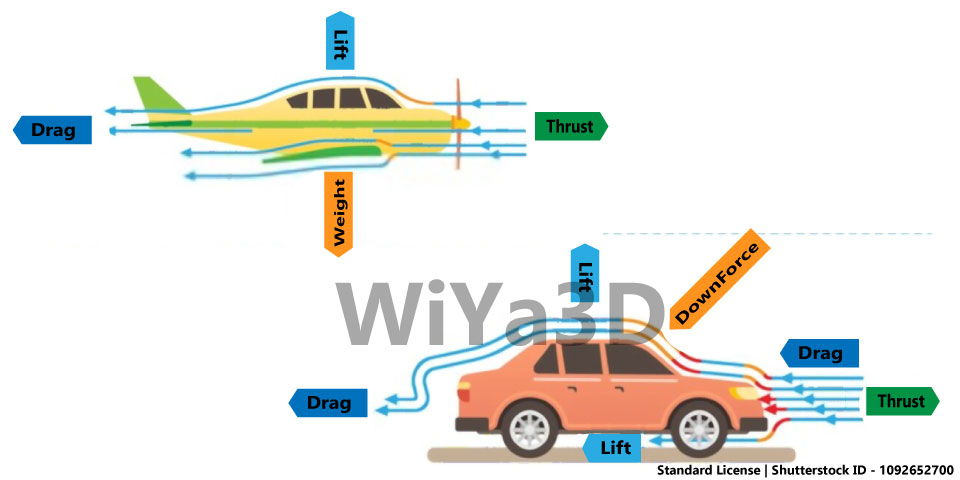
Obstacles in Aerodynamics
DRAG
Another important principle in aerodynamics is the idea of drag. Drag is the resistance that air exerts on an object as it moves through it. A vehicle with a streamlined shape will experience less drag than a boxy vehicle, allowing it to move more efficiently.
The flow on the moving body has a combined effect of both pressure force and wall shear, that causes the overall drag force. The friction drag is caused by wall shear stress, while the pressure-induced drag is known as the pressure drag.
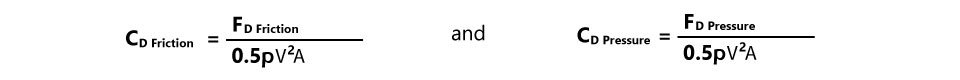
Here V is the relative free stream air velocity, FD is the drag force, ρ is the density, and A is the cross-sectional area in the flow direction.
Whenever a solid body moves in the air, drag is one of the main obstacles. A road vehicle accelerates and burns fuel, drag force pushes the vehicle back from the front and pulls it from the rear to reduce speed, in result fuel efficiency is adversely affected. During these adversative effects, fuel energy is lost by approximately 50-60%. The reduction of this drag force has become one of the main concerns in road vehicle production.
LIFT
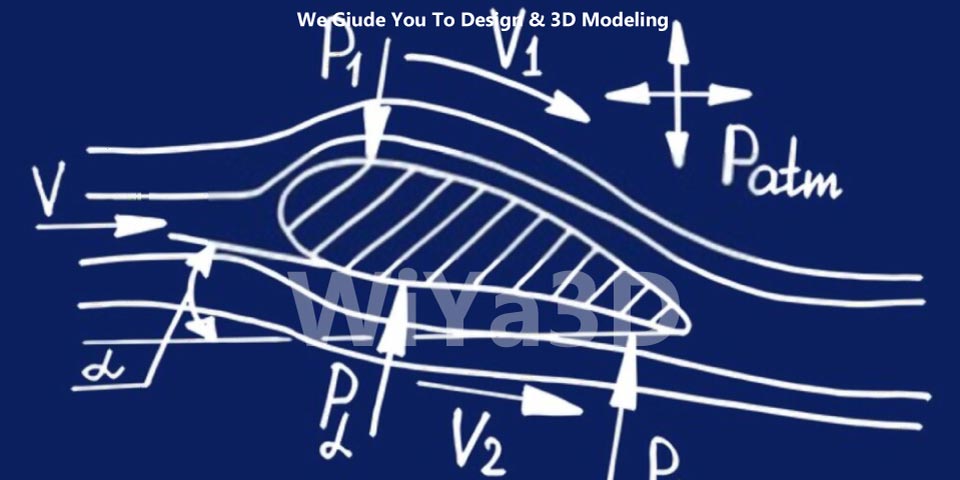
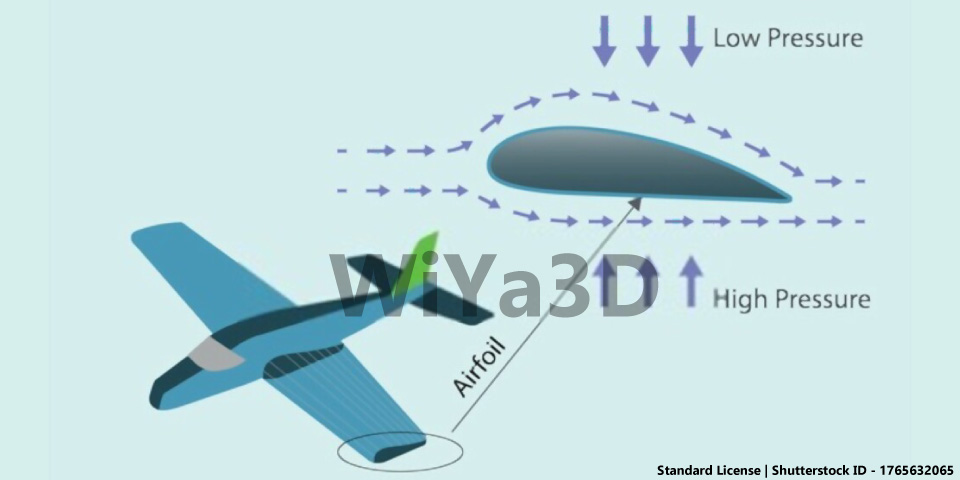
One of the key principles of aerodynamics is the concept of lift. Lift is the force that allows an object to rise into the air, and it is created by the difference in air pressure on the top and bottom of an object. By carefully designing the shape of an object, engineers can create lift and make the object more aerodynamic. It is important to keep the downforce in balance. The downforce generation follows the equation of Bernoulli expressed as
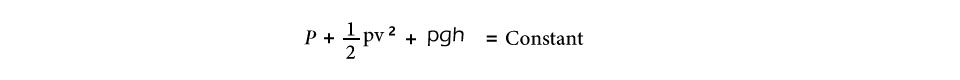
The Bernoulli equation is constant along with a streamlined flow. There are two types of flows; laminar and turbulent flow. Laminar flow is a smooth and streamlined flow where the adjacent layers of fluid slide each other and follow the path of the particles ahead. Velocity and dynamic pressure are directly related to each other. The flow around an airfoil, generating positive lift.
From a designer’s perspective, only the drag coefficient (Cd) and frontal area (A) can be controlled. While designing a vehicle, reducing the frontal area will considerably decrease drag force. In the development of a successful design, aerodynamics has nowadays become the dominant factor.
Thrust
Thrust is the opposite of drag. Thrust can propel a small aircraft. Jet engines could provide propulsion for a larger aero-plane. It can only fly until it slowed down and landed by the drag.
How Can We Get The Best Aerodynamic Design
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is an effective tool that saves a lot of time and a significant amount of money. Computational Fluid Dynamics analysis is helpful to achieve good aerodynamic results.
- The most significant advantage of using CFD tools is that the outcomes can be obtained without the need for a prototype. This is important because it has the potential to reduce the expense of manufacturing commercial vehicles.
- The main benefit that we can get while using CFD is the faster evaluation of new ideas, few intuitions into our process and performance, save time and cost, increase customer confidence, maximize the effectiveness of our manufacturing resources, business advantages, increase credibility with customers, and get better results.
Benefits of Aerodynamic design
Decrease Fuel Consumption
According to various studies, reducing drag will save a significant amount of fuel. Designers know that using a precise aerodynamic design will minimize drag.
Reduce Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Emmision
Significantly reducing fuel consumption can help to minimize CO2 emissions. By using the accurate aerodynamic design, fuel consumption can be minimised. It was also discovered that using aerodynamic devices is the easiest way to control Co2 emissions.
Cost Reduction
Costs can be reduced by improving the design. The cost savings will be more significant if the design is more aerodynamically suited. This suggests that decisions made early in the design process have the maximum impact on the technical and financial success of the product.
Concluding Remarks
Air resistance is reduced by enhancing the aerodynamics of an electric car, leading to improved mileage or the range that a vehicle can drive. According to a Tesla Inc. report, a 10% improvement in aerodynamic efficiency will result in a 5% increase in capacity. Aerodynamics is much more critical for aeroplanes and space rockets. As spacecraft return to Earth, they travel at high speeds from the virtual vacuum of space into the Earth’s atmosphere, where they are unbearably heated.
Aerodynamics is important to the rest of us as well. If you are a professional cyclist who wants to win a race, you must use all of your energy to lose as much air as possible. Reducing air resistance is one of the simplest ways to save fuel, resources, and the environment. In short, the aerodynamic design will increase the stability of moving objects.